
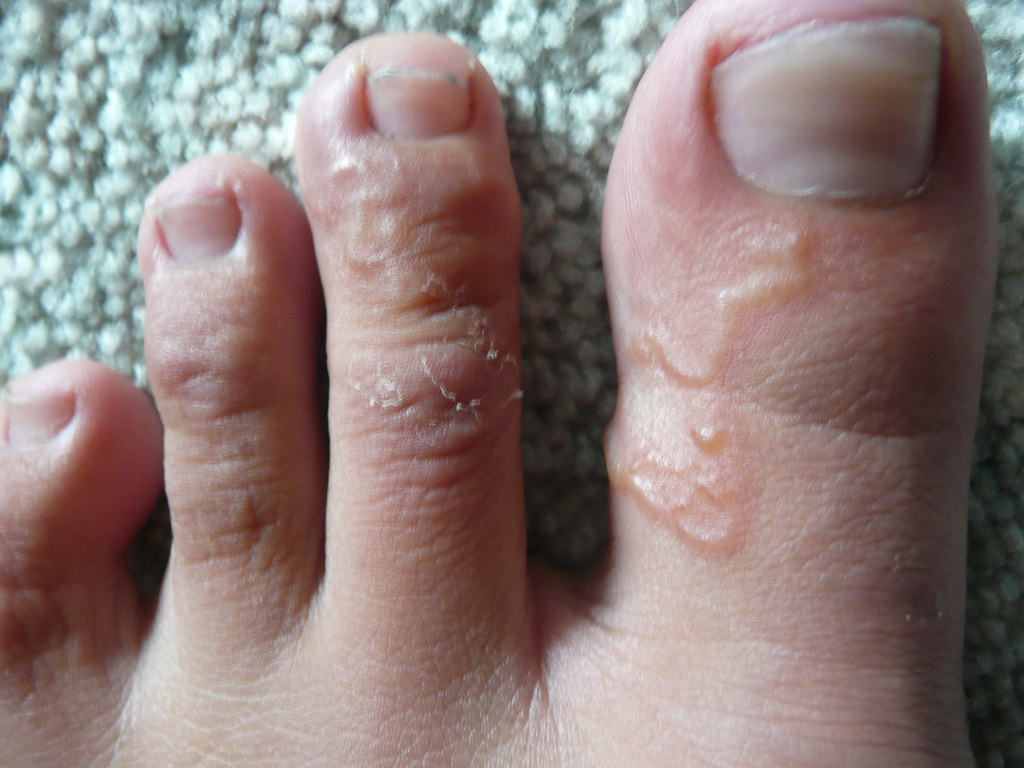
Large hookworms in humans skin#
Skin exposure to water contaminated with infected freshwater snails

Schistosomiasis – bilharzia, bilharziosis or snail fever (all types)Īfrica, Caribbean, eastern South America, east Asia, Middle East – 200 million people Ingestion of raw or undercooked freshwater crabs crayfishes or other crustaceans Paragonimus westermani Paragonimus africanus Paragonimus caliensis Paragonimus kellicotti Paragonimus skrjabini Paragonimus uterobilateralis Opisthorchis viverrini, Opisthorchis felineus, Clonorchis sinensisĬonsuming infected raw, slightly salted or frozen fish Siberia, Manchuria, Balkan states, Israel, Spain Ingestion of infested water plants or water (intermediate host:amphibic snails) Ingestion of under prepared freshwater fishįasciola hepatica in Europe, Africa, Australia, the Americas and Oceania Fasciola gigantica only in Africa and Asia, 2.4 million people infected by both species Gall bladder ducts and inflammation of liver Ingestion of material contaminated with infected dog or cat feces (humans: dead-end host)įlukes Common name of organism or diseaseĬlonorchis sinensis Clonorchis viverrini Ingestion of material contaminated by flour beetles, mealworms, cockroachesīrain, muscle, Eye (Cysts in conjuntiva/anterior chamber/sub-retinal space)Īsia, Africa, South America, Southern Europe, North America. Imaging of hydatid cysts in the liver, lungs, kidney and spleenĪs intermediate host, ingestion of material contaminated by feces from a carnivore as definite host, ingestion of uncooked meat ( offal) from a herbivore Tapeworms Common name of organism or diseaseĮchinococcus granulosus, Echinococcus multilocularis, E. Helminth organisms (also called helminths or intestinal worms) include: Triatoma/ Reduviidae – "kissing bug" insect vector, feeds at night Mexico, Central America, South America – 16–18 million Tsetse fly, day-biting fly of the genus GlossinaĬolon, esophagus, heart, nerves, muscle and blood Microscopic examination of chancre fluid, lymph node aspirates, blood, bone marrowĥ0,000 to 70,000 people only found in Africa
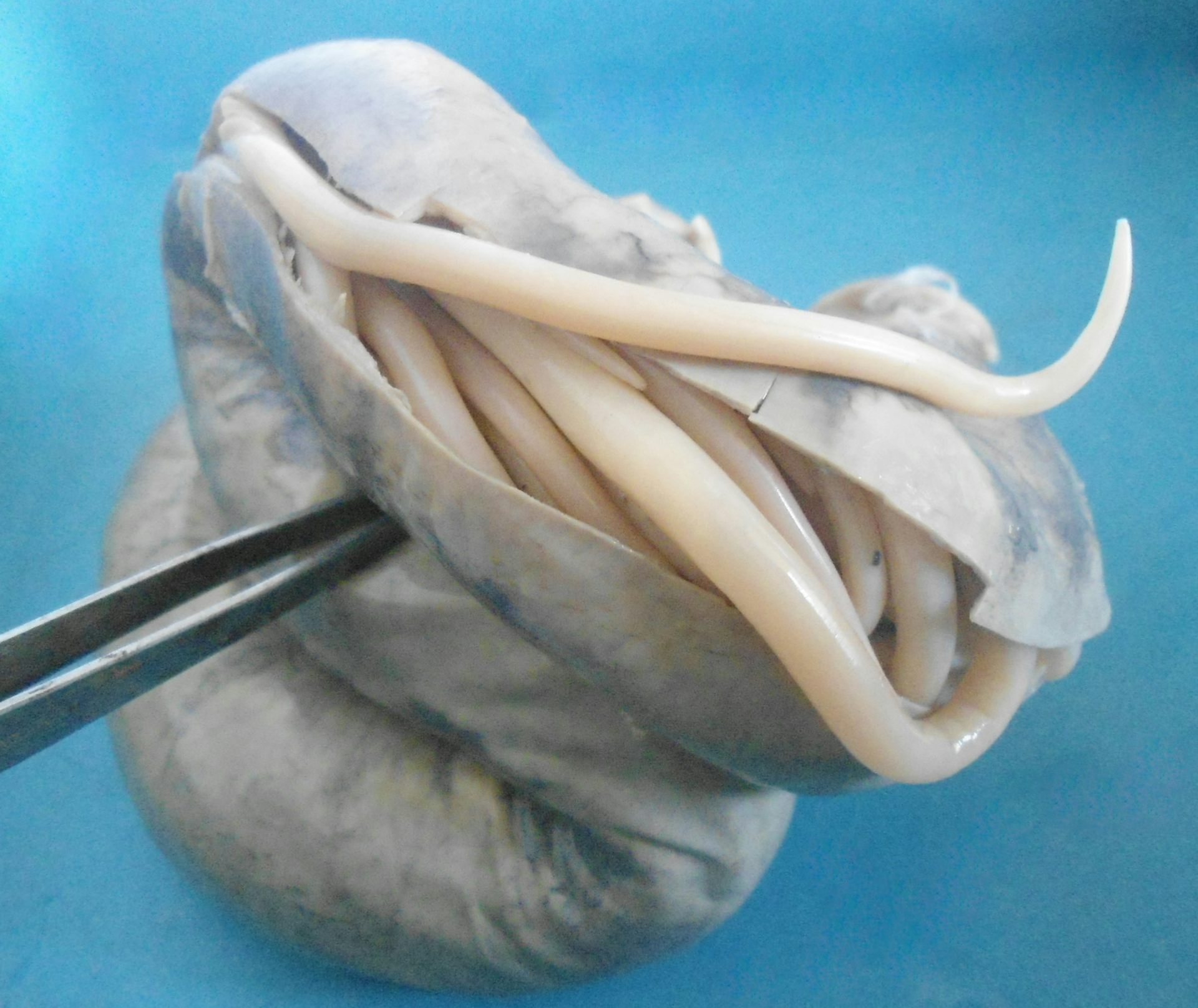
Sexually transmitted infection – only trophozoite form (no cysts) Ingestion of uncooked/undercooked pork/lamb/goat with Toxoplasma bradyzoites, ingestion of raw milk with Toxoplasma tachyzoites, ingestion of contaminated water food or soil with oocysts in cat feces that is more than one day oldįemale urogenital tract (males asymptomatic) Worldwide: one of the most common human parasites estimated to infect between 30–50% of the global population. Ingestion of uncooked/undercooked beef/pork with Sarcocystis sarcocysts Sarcocystis bovihominis, Sarcocystis suihominis Nasal mucosa came into contact with infected material through bathing in common ponds Plasmodium falciparum (80% of cases), Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale curtisi, Plasmodium ovale wallikeri, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium knowlesi Nasal insufflation of contaminated warm fresh water, poorly chlorinated swimming pools, hot springs, soil Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) Phlebotomus, Lutzomyia – bite of several species of phlebotomine sandflies Visceral leishmaniasis – worldwide cutaneous leishmaniasis – Old World mucocutaneous leishmaniasis – New World Visual identification of lesion or microscopic stain with Leishman's or Giemsa's stain Worldwide – less common than Toxoplasma or Cryptosporidiumįecal oral route – ingestion of sporulated oocyst Ingestion of water containing deer or beaver feces Stool (fresh diarrheic stools have amoeba, solid stool has cyst)Īreas with poor sanitation, high population density and tropical regionsįecal-oral transmission of cyst, not amoeba Intestines (mainly colon, but can cause liver failure if not treated) Ingesting water or food contaminated with feces Ingestion of oocyst thru contaminated food Ingestion of oocyst (sporulated), some species are zoonotic (e.g.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
